Our Joint Partnership with Cospas-Sarsat
Click image to zoom
Central to the success of Cospas-Sarsat is the number of international satellites that can transmit 406 distress alert data to ground stations and MCCs around the world.
Note: Satellite constellations in the system but not shown here are Electro, INSAT, Louch and MSG.
A World-Wide System
Cospas-Sarsat is an international, humanitarian search and rescue system that uses space-based technology to detect and locate 406 emergency beacons carried by ships, aircraft, or individuals venturing into remote areas, often inaccessible by mobile phone.
The system consists of a network of satellites, ground stations, mission control centers (MCCs), and rescue coordination centers (RCCs) that work together when a 406 beacon is activated. The United States is one of the four founding members of Cospas-Sarsat.
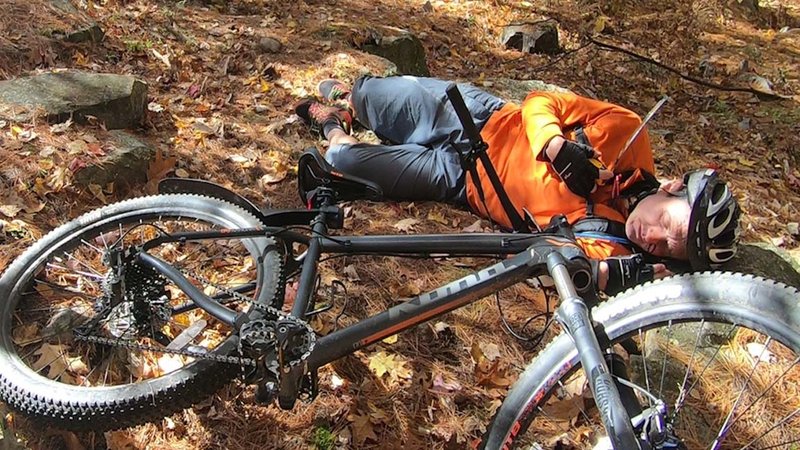

SAR-Ex Simulation images courtesy of Cospas-Sarsat

Here’s how it works. When someone in a distress situation sets off their 406 beacon, the signal is received by a satellite and relayed to the nearest available ground station. The ground station, called a Local User Terminal, or LUT, processes the signal and calculates the 406 beacon’s position.
This position is transmitted to the closest MCC along with identification data and other information extracted from the 406 beacon signal. The MCC then transmits an alert message to the closest RCC based on the geographic location of the 406 beacon signal. The RCC is responsible for organizing the search and rescue (SAR) team that will carry out the rescue. If the 406 beacon is registered to another country, then that country’s MCC is also notified.
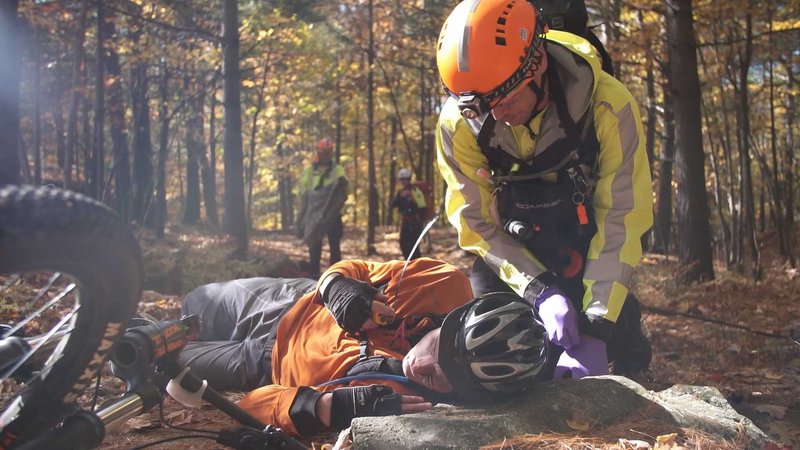

SAR-Ex Simulation images courtesy of Cospas-Sarsat
What contributes to the effectiveness and efficiency of the Cospas-Sarsat System is the fact that it sets very strict technical specifications and protocols for all ground system and satellite system receiver and transmitter components. It also is responsible for setting 406 beacon standards including bandwidth, signal strength, battery life and performance requirements specific to beacon type.
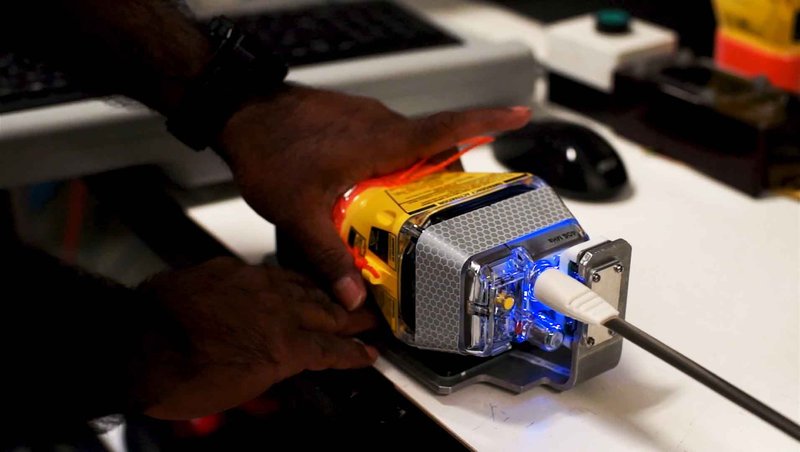

Image courtesy of Cospas-Sarsat
Beacon testing before shipment is just one aspect of the quality control Cospas-Sarsat requires for all technology and systems in its programme.
Beacon types vary by user application. 406 ELT (Emergency Locator Transmitter) beacons are for aviation use. EPIRBs (Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon) for maritime use, and PLBs (Personal Locator Beacon) for personal use during wilderness activities. There are three types of satellites used for Search and Rescue Satellite-Aided Tracking: MEOSAR (medium earth orbiting) satellites, LEOSAR (Low earth-orbiting) satellites, and GEOSAR (geostationary) satellites.
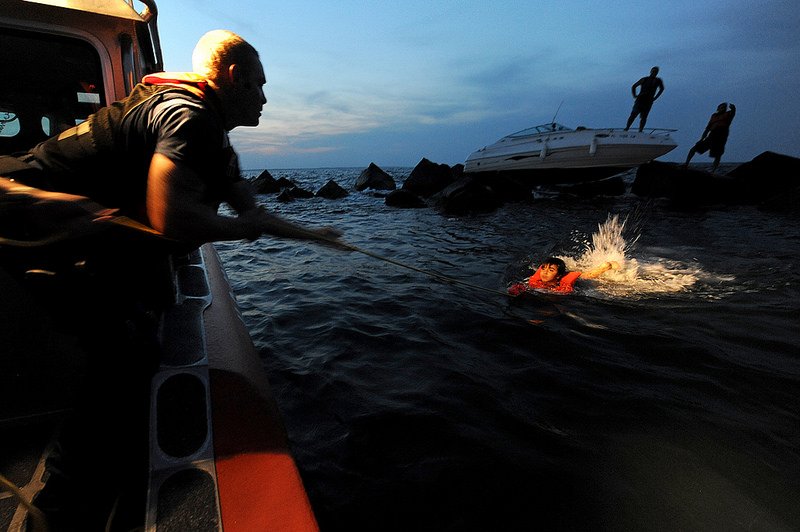

Image courtesy of DIVDs
Due to the global reach of Cospas-Sarsat, American citizens can be assured that if they activate their registered 406 beacon anywhere around the world, their distress call will be heard.
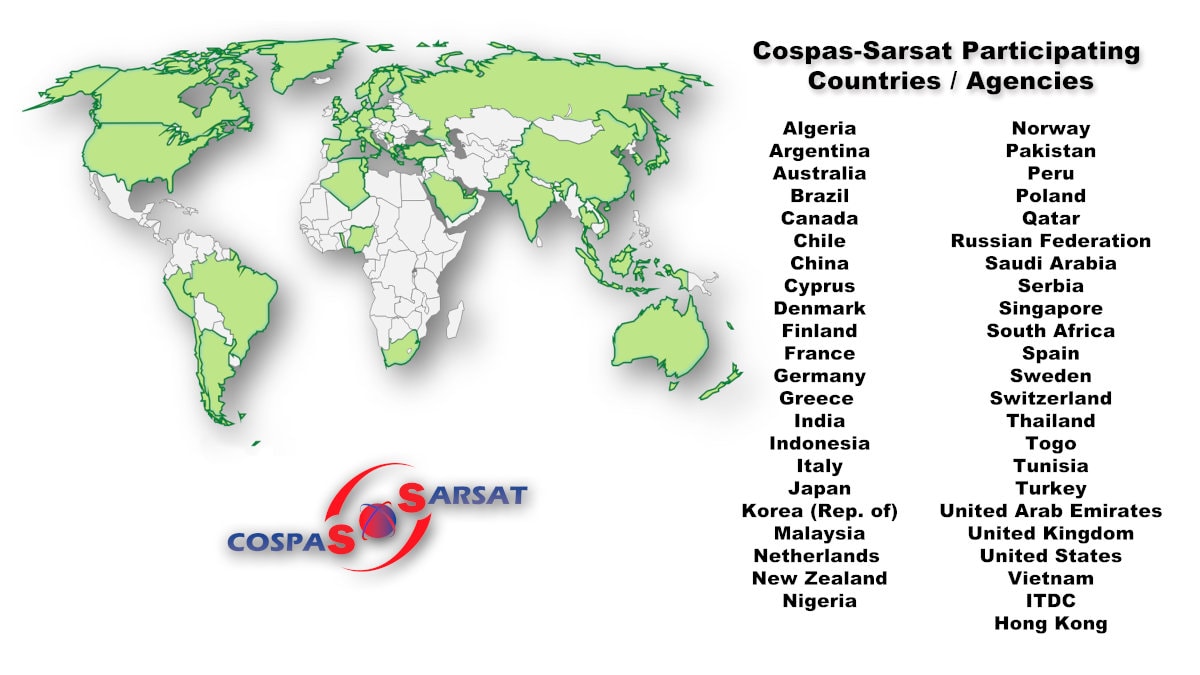
The benefits to U.S. participation in the international Cospas-Sarsat program are substantial. With 45 countries onboard, sharing space and ground technologies and resources, it is the only system that provides consistent worldwide coverage no matter where the 406 beacon was purchased, registered, or activated. There are no additional user or subscription fees beyond the purchase of the 406 beacon itself. Even registration is free.
The Cospas-Sarsat system provides a tremendous resource and unparalleled reach for protecting the lives of aviators, mariners and outdoor adventurers that was unimaginable prior to the Space-Age. With the press of a button a distress message can be sent from a 406 MHz emergency beacon to the appropriate search and rescue (SAR) authorities, regardless of weather or terrain conditions, from anywhere on Earth, 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.
Cospas-Sarsat – We save lives.